- Home
- Underwater wrecks
- Ancient wrecks
- Pointe de la Luque 2 (Marseille)
Approximate location of the Pointe de la Luque 2 wreck in Marseille.
Description
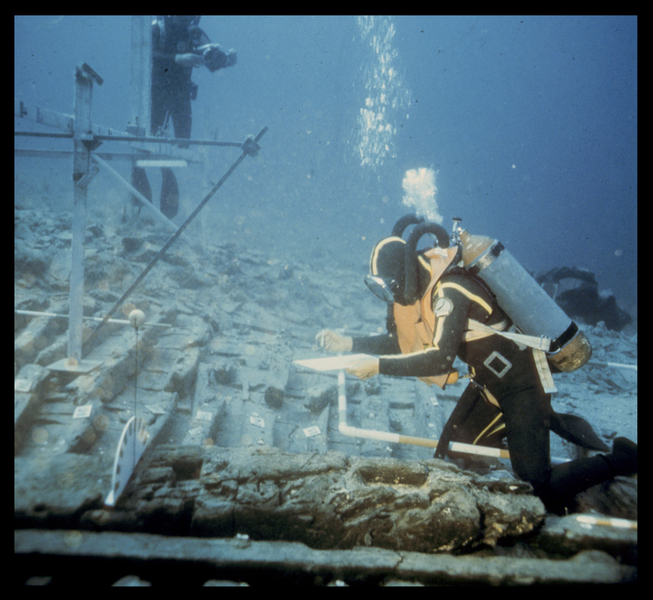
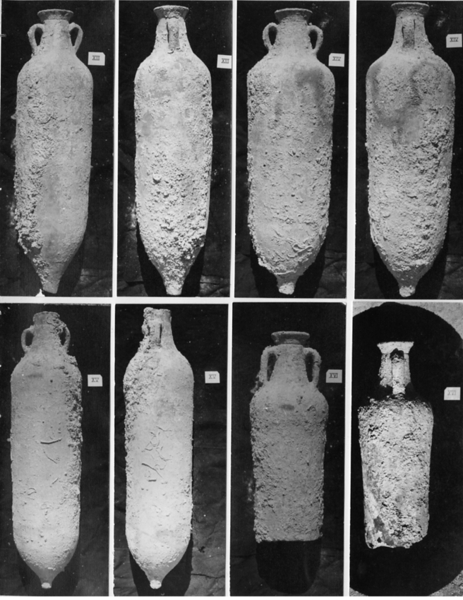
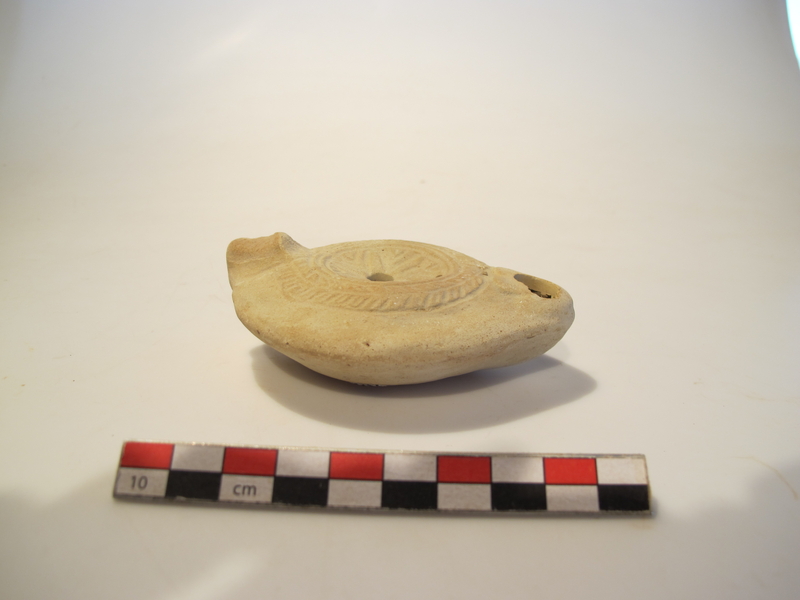
The remains of Pointe de la Luque 2 (or B) lay scattered 30–40 m below the sea to the northwest of the island of Pomègues (Frioul, Marseilles). In addition to oil lamps (a great many of which are marked) and cylindrical African amphorae (some bearing the signature of potters in Mauretania Caesariensis, now Algeria), archaeologists discovered a well-preserved hull dating from the middle of the fourth century. Discovered and reported in 1970, the wreck was excavated in 1971–74 with the help of DRASSM and the French Navy. Part of the hull lay in a shallower zone to the east and was covered with fragments of amphorae and lamps. A rich cargo was situated further down, to the northwest. Given that a large section of the hull had been preserved, it was decided to trial one of the first integrated underwater photogrammetry systems. The site was reopened in 1992 by the Centre Camille Jullian and the Mediterranean Institute for Ecology and Palaeoecology (IMEP), a CNRS research unit, to sample and analyse the wood.
Underwater view of divers recording the hull
© Jean-Claude Négrel/DRASSM
Selection of African amphorae discovered in 1974.
© Jean-Claude Négrel/DRASSM
Fine example of an African oil lamp.
© Patrick Glotain / Drassm
Operation managers
- Jean-Claude Négrel (1971-1974)
- Patrice Pomey/CNRS (1992)
Bibliography
- DOVIS-VICENTE Catherine — Étude du commerce maritime au IVe siècle : cas de l’épave de la Luque B. Villeneuve-d’Ascq : Presses Universitaires du Septentrion, 2001.
- Pointe de la Luque 2 - shipwreck